C# For Kids
Unlock the magic of coding with ‘Coding Adventures: A Kid’s Guide to Programming with C#’! Packed with fun activities and hands-on projects, this engaging ebook introduces young readers to the exciting world of computer programming using the C# language. From basic concepts to building interactive games, it’s the perfect guide for budding young coders ready…
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, two innovations are transforming the way we interact with the world: Cloud Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT). Individually, these technologies are already revolutionizing industries, but when combined, they create a powerful synergy that drives unprecedented levels of efficiency, connectivity, and innovation. This article explores how Cloud Computing and IoT work together and provides real-world examples of their combined impact.
Understanding Cloud Computing and IoT
Cloud Computing
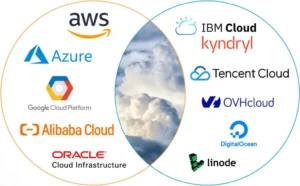
Cloud Computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). This technology allows for on-demand access to resources, enabling businesses to scale and innovate without investing heavily in physical infrastructure.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT encompasses a network of interconnected physical devices that collect and exchange data via the internet. These devices range from household appliances and wearable health monitors to industrial sensors and smart city infrastructure. IoT devices gather real-time data that can be analyzed to make informed decisions, enhance operations, and improve quality of life.
The Synergy of Cloud Computing and IoT
When IoT devices are integrated with Cloud Computing, the benefits multiply:
- Scalability: Cloud platforms provide the necessary infrastructure to support the massive data generated by IoT devices. This scalability ensures that as the number of devices grows, the system can handle increased data loads without compromising performance.
- Data Storage and Processing: Cloud services offer vast storage capabilities and powerful processing power. IoT devices can offload data to the cloud, where it can be stored and analyzed. This enables real-time data processing and long-term data retention without overwhelming local resources.
- Accessibility and Integration: Cloud Computing ensures that IoT data is accessible from anywhere, at any time. This accessibility allows for seamless integration of IoT data with other systems and applications, facilitating advanced analytics and insights.
- Cost Efficiency: Using cloud services, businesses can reduce costs associated with maintaining physical servers and infrastructure. Cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go models, allowing companies to pay only for the resources they use.
Real-World Examples
Smart Agriculture
In smart agriculture, IoT devices such as soil sensors, weather stations, and drones collect data on soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and crop health. This data is sent to cloud-based platforms for analysis. Farmers can access this information via mobile apps to make data-driven decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. For instance, precision agriculture company John Deere uses cloud-based IoT solutions to optimize crop yields and reduce resource usage.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor patients’ vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. This data is transmitted to the cloud, where healthcare providers can monitor patients remotely and in real time. Companies like Philips Healthcare use cloud-IoT integrations to offer remote patient monitoring services, enhancing patient care and reducing hospital visits.
Smart Cities
Smart city initiatives leverage IoT devices to collect data on traffic flow, energy usage, and environmental conditions. This data is analyzed in the cloud to optimize urban infrastructure and services. For example, Barcelona has implemented a smart lighting system that uses IoT sensors to adjust street lighting based on real-time pedestrian and vehicle movement data, resulting in significant energy savings.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
In manufacturing, IoT sensors monitor equipment performance and environmental conditions on the factory floor. This data is uploaded to cloud platforms for predictive maintenance and operational optimization. General Electric (GE) utilizes cloud-IoT solutions to monitor the health of industrial machinery, predict failures, and schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur, thereby minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
The Future of Cloud Computing and IoT
The integration of Cloud Computing and IoT is set to drive the next wave of digital transformation. Emerging technologies like edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and 5G will further enhance this synergy. Edge computing will bring computation closer to IoT devices, reducing latency and improving response times. AI will enable more sophisticated data analysis and decision-making, while 5G will provide the high-speed, low-latency connectivity necessary for real-time IoT applications.
Conclusion
The combination of Cloud Computing and IoT represents a powerful duo poised to reshape industries and improve our daily lives. By leveraging the scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency of cloud platforms, alongside the data-rich environment of IoT devices, businesses and communities can unlock new levels of innovation and productivity. As these technologies continue to evolve, their integrated potential will drive the future of smart solutions and connected experiences.